Why do middle-aged and elderly people need to do carotid ultrasound?
Автор публикации: NiuKevin, дата:
Carotid ultrasound is one of the effective methods for diagnosing and evaluating carotid wall lesions. It plays a key role in the epidemiological investigation of atherosclerosis and the evaluation of the effectiveness of atherosclerosis prevention and treatment trials.
Carotid artery color Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive method for examination. It is simple and safe. It can detect carotid artery disease at an early stage and evaluate the degree of disease. It can not only provide morphological information of atherosclerotic plaque, but also provide plaque-induced hemodynamic changes. The information has important guiding role in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with carotid artery disease, and is also a good follow-up tool for carotid artery interventional or endarterectomy. It is currently the preferred method for screening carotid artery diseases.
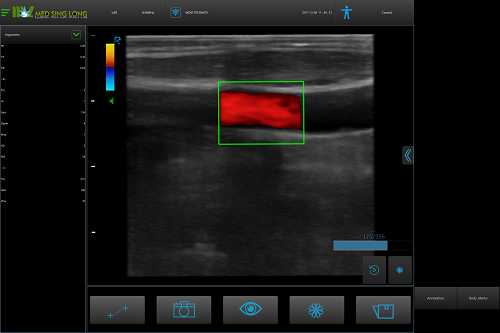
Carotid artery color Doppler ultrasound combined with TCD detection technology can timely and accurately observe intracranial and extrahemodynamic changes of ischemic cerebrovascular production, which can improve the detection rate and diagnostic accuracy of intracranial and extracranial cerebral vascular diseases. Provide reliable and objective imaging and kinetic basis for clinical selection of different treatments and effective treatment outcomes.
Carotid atherosclerosis is the most common vascular disease in the middle-aged and elderly population. The formation of vascular atherosclerotic plaque easily leads to stenosis, occlusion, and embolus formation. It is closely related to transient ischemic attack and ischemic stroke. Related.
Among the middle-aged and elderly people, if there is hyperlipidemia, hypertension, diabetes, and a history of fainting, they often feel dizziness, pain, and early manifestations of stroke (transient black eyes, numbness of one limb, language disorder, sudden mouth tilt, etc.) It is very necessary to do carotid ultrasound.
